When Did the US Enter World War II? A Comprehensive Timeline and Analysis
- Understanding the Context: When Did the US Enter WW2?
- The Attack on Pearl Harbor: A Turning Point for US Involvement in WW2
- Key Dates and Events Leading to the US Entry into World War II
- Impact of US Entry into WW2 on the Global Conflict
- Frequently Asked Questions About the US Entry into World War II
Understanding the Context: When Did the US Enter WW2?
The United States officially entered World War II on December 7, 1941, following the surprise attack on Pearl Harbor by the Japanese Imperial Navy. This pivotal event marked a significant turning point in the war, shifting the US from a position of neutrality to active involvement. Prior to this, the US had maintained a policy of isolationism, largely influenced by the aftermath of World War I and the Great Depression. However, growing tensions in Europe and Asia, along with increasing support for Allied nations through programs like Lend-Lease, set the stage for eventual engagement.
The attack on Pearl Harbor not only resulted in the destruction of a significant portion of the US Pacific Fleet but also galvanized public opinion in favor of entering the war. In the immediate aftermath, President Franklin D. Roosevelt delivered a famous speech to Congress on December 8, 1941, declaring December 7th as "a date which will live in infamy." The swift passage of the war declaration against Japan marked the beginning of a more expansive military engagement for the United States.
Following the declaration of war on Japan, Germany and Italy declared war on the United States on December 11, 1941. This led to a full-scale involvement of American forces across multiple theaters of war, including the Pacific and European fronts. The US military mobilization was unprecedented, resulting in the rapid expansion of armed forces and industrial production to support the war effort.
The entry of the United States into World War II had profound implications, not only for the course of the conflict but also for the global balance of power in the post-war era. The US became a key player in the Allied forces, contributing significantly to the eventual defeat of the Axis powers through a combination of military strategy, economic strength, and technological innovation.
The Attack on Pearl Harbor: A Turning Point for US Involvement in WW2
The attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, marked a significant turning point in the United States' involvement in World War II. Prior to this event, the U.S. had maintained a position of neutrality, focusing primarily on domestic issues and avoiding direct engagement in the escalating global conflict. However, the surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy catalyzed a dramatic shift in public opinion and government policy, propelling the nation into full-scale war.
Key Factors of the Attack:
- Surprise Assault: The attack was unexpected, occurring on a peaceful Sunday morning, which led to extensive damage to the U.S. Pacific Fleet.
- Significant Losses: Over 2,400 Americans were killed, and numerous ships and aircraft were destroyed, showcasing the vulnerability of American military defenses.
- Unity and Resolve: The attack united a previously divided nation, igniting a sense of patriotism and urgency to respond to the aggression.
In the aftermath of Pearl Harbor, President Franklin D. Roosevelt addressed Congress, famously declaring December 7th as "a date which will live in infamy." This speech galvanized the American public and led to a swift declaration of war against Japan on December 8, 1941. Subsequently, Germany and Italy declared war on the United States, further solidifying America’s role in the global conflict. The attack on Pearl Harbor not only marked the entry of the U.S. into World War II but also fundamentally altered the course of the war, as American industrial and military resources were mobilized on an unprecedented scale.
The implications of the attack extended beyond immediate military responses; it reshaped American foreign policy and military strategy for years to come. The U.S. transitioned from isolationism to a leading role in global affairs, committing significant resources to the Allied powers. This shift not only impacted the trajectory of World War II but also established the United States as a dominant force in post-war geopolitics, influencing international relations for decades.
Key Dates and Events Leading to the US Entry into World War II
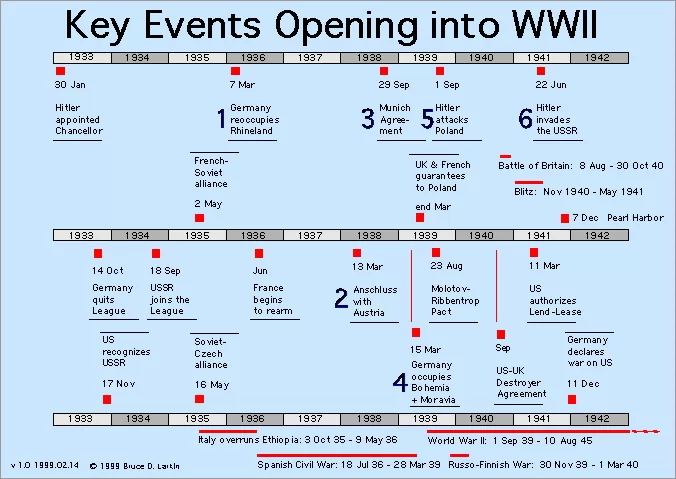
The journey to the United States' entry into World War II was marked by a series of pivotal events and dates that shaped the nation's response to global conflicts. One of the earliest significant events was the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany on September 1, 1939. This aggressive action prompted Britain and France to declare war on Germany, marking the official start of World War II in Europe. While the United States maintained a policy of neutrality at this stage, the global situation began to shift public opinion and government policy.
Another crucial date was March 11, 1941, when President Franklin D. Roosevelt signed the Lend-Lease Act into law. This legislation allowed the U.S. to supply military aid to foreign nations whose defense was deemed vital to American security. The act primarily supported the United Kingdom and later the Soviet Union, indicating a significant shift towards involvement in the war, even as the U.S. remained officially neutral.
The turning point came on December 7, 1941, with the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. This surprise military strike resulted in significant losses for the U.S. Pacific Fleet and galvanized public sentiment towards war. The following day, December 8, 1941, President Roosevelt addressed Congress, leading to the declaration of war against Japan. This event not only marked the U.S. entry into World War II but also set the stage for the nation’s full-scale mobilization for the conflict.
Additionally, the Axis powers' aggression throughout 1941, including Germany's declaration of war against the United States on December 11, further entrenched America's involvement in the global conflict. These key dates and events illustrate the complex interplay of international relations and domestic sentiments that ultimately led the U.S. to join the fight against tyranny and aggression during World War II.
Impact of US Entry into WW2 on the Global Conflict
The entry of the United States into World War II in December 1941 marked a pivotal moment in the global conflict, significantly altering the dynamics of warfare and international relations. Following the attack on Pearl Harbor, the U.S. mobilized its vast industrial and military resources, shifting the balance of power in favor of the Allies. This influx of American troops, supplies, and technology invigorated the Allied forces, which were struggling against the Axis powers.
Military Contributions
The U.S. military's involvement brought about substantial changes on various fronts. Key contributions included:
- Deployment of Troops: Millions of American soldiers were deployed to fight in Europe and the Pacific, providing much-needed manpower.
- Material Support: The U.S. supplied the Allies with weapons, vehicles, and other essential materials through programs like Lend-Lease.
- Strategic Bombing: American air power played a crucial role in disrupting Axis supply lines and infrastructure.
The U.S. also introduced new military strategies and technologies, including aircraft carriers and advanced bombers, which had a profound impact on naval and aerial combat. This technological edge allowed the Allies to gain momentum in critical battles such as Midway and D-Day.
Economic Influence
Economically, the U.S. entry into the war transformed its own economy and that of the global landscape. The war effort stimulated American industries, leading to:
- Increased Production: Factories shifted from consumer goods to military production, creating jobs and boosting the economy.
- Global Trade Networks: The U.S. emerged as a key supplier for the Allies, solidifying its position as an economic superpower.
- Post-War Reconstruction: The U.S. played a significant role in shaping post-war recovery efforts through initiatives like the Marshall Plan.
This economic might not only supported the war effort but also laid the foundation for the U.S. to become a leading force in global politics in the subsequent decades.
Geopolitical Shifts
The U.S. entry into WWII also prompted significant geopolitical shifts. The collaboration among the Allies fostered new international relationships and institutions. The war united nations against common foes, leading to the establishment of organizations aimed at promoting peace and cooperation, such as the United Nations. The U.S. emerged as a dominant force in this new world order, counterbalancing the influence of the Soviet Union and shaping the course of international relations for years to come.
The combined military, economic, and political impacts of the U.S. entry into World War II not only influenced the outcome of the conflict but also redefined the global landscape in the latter half of the 20th century.
Frequently Asked Questions About the US Entry into World War II
What event prompted the US to enter World War II?
The primary event that led to the United States' entry into World War II was the surprise attack on Pearl Harbor by the Japanese on December 7, 1941. This attack resulted in significant loss of life and damage to the US Pacific Fleet, prompting President Franklin D. Roosevelt to call for a declaration of war against Japan the following day. The attack galvanized public opinion and shifted the US from a position of isolationism to active involvement in the conflict.
What were the US's initial military actions after entering the war?
After declaring war on Japan, the United States quickly mobilized its military forces. Initial actions included:
- Defensive operations in the Pacific: The US focused on defending its territories and assets in the Pacific, including the Philippines and Guam.
- Strategic bombings: The US began conducting air raids against Japanese-held territories to disrupt their military operations.
- Alliances: The US strengthened its alliances with the United Kingdom and other Allied nations to coordinate military efforts against the Axis powers.
How did public opinion in the US shift regarding the war?
Before Pearl Harbor, many Americans were isolationist and preferred to avoid involvement in foreign conflicts. However, the attack changed public sentiment dramatically. The following factors contributed to this shift:
- Increased patriotism: The attack on Pearl Harbor unified the nation, fostering a sense of patriotism and a desire to support the war effort.
- Media coverage: Graphic media reports of the attack and its aftermath played a crucial role in mobilizing public support for military action.
- Government propaganda: The US government launched extensive propaganda campaigns to encourage enlistment and war production.
What were the long-term effects of the US entering World War II?
The entry of the United States into World War II had significant long-term effects, both domestically and internationally. The US emerged as a global superpower, leading to its involvement in international politics for decades to come. Additionally, the war effort led to technological advancements and economic growth, which laid the foundation for the post-war boom. The experience also fostered a sense of unity among diverse groups within the country, shaping the future social landscape of the United States.
